


Cyber security is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and sensitive data from digital attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches. In 2025, as businesses, governments, and individuals become increasingly reliant on technology, cyber threats are growing at an unprecedented rate.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making cyber security not just a technical concern but a critical business priority.
This guide covers everything you need to know and from the most common cyber threats to best practices and future trends, so you can stay one step ahead.
Cyber security is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. These attacks aim to access, steal, or destroy sensitive information, disrupt operations, or extort money from users or businesses.
In simple terms, cyber security is your digital shield, safeguarding everything from your personal devices to an organization’s IT infrastructure.
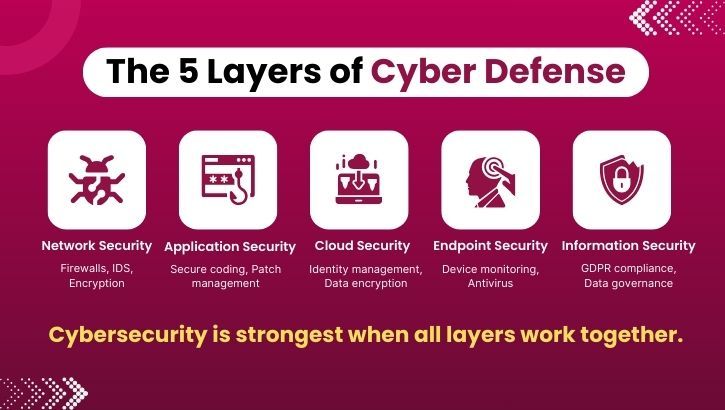
Cyber security isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It consists of multiple layers, each focusing on a specific area of protection:
1. Network Security
This protects internal networks from intruders, whether malicious attackers or opportunistic malware. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption are key elements of network security.
2. Application Security
Applications can be a gateway for hackers if left unprotected. Secure coding practices, regular software updates, and vulnerability testing are used to minimize risk.
3. Cloud Security
As more businesses move to the cloud, protecting data stored there has become critical. Cloud security involves encryption, identity management, and regular monitoring to prevent breaches.
4. Endpoint Security
Endpoints such as laptops, mobile phones, and IoT devices are often the easiest targets for hackers. Endpoint security tools include antivirus programs, device monitoring, and strict access controls.
5. Information Security (InfoSec)
This ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Strong data security policies and compliance with regulations like GDPR are part of this layer.
6. Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity
Even with strong security, incidents can still occur. Disaster recovery plans ensure a business can quickly restore operations and minimize damage after an attack.
| Cyber Threat | Description | Real-World Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage or steal data. | WannaCry ransomware infected 230,000 computers in 2017 | System lockouts, financial losses, data theft |
| Phishing | Fake emails/messages trick users into revealing data. | 2022 Microsoft phishing campaign targeting 10k firms | Credential theft, account compromise |
| Ransomware | Encrypts data until ransom is paid. | Colonial Pipeline attack in 2021 disrupted fuel supply | Service disruption, ransom payments |
| DDoS Attack | Overwhelms network with fake traffic to cause downtime | 2023 attack on gaming network caused hours-long outage | Website downtime, revenue loss |
| Insider Threats | Employees or contractors misuse their access. | Twitter’s 2020 breach via insider account compromise | Data leaks, reputational damage |
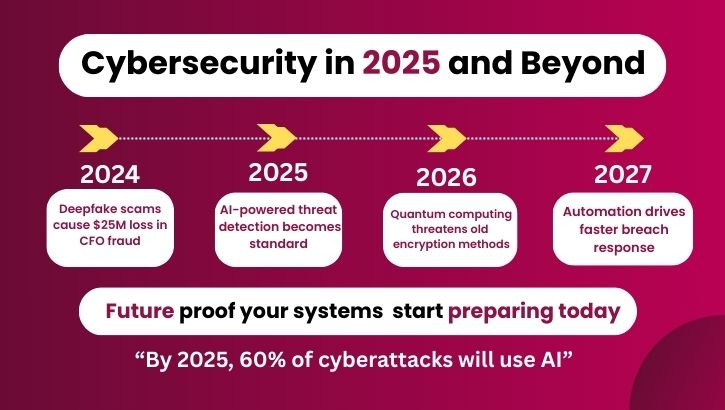
| Social Engineering | Manipulating human trust to gain access to systems. | Deepfake CFO video scam costing $25M in 2024 | Unauthorized fund transfers, fraud |
Case Study: In 2024, a well-known manufacturing company suffered a ransomware attack that shut down production for three days, costing $5M in lost revenue. The breach was traced to an employee clicking a phishing link, a reminder that human error is still the #1 cyber risk.
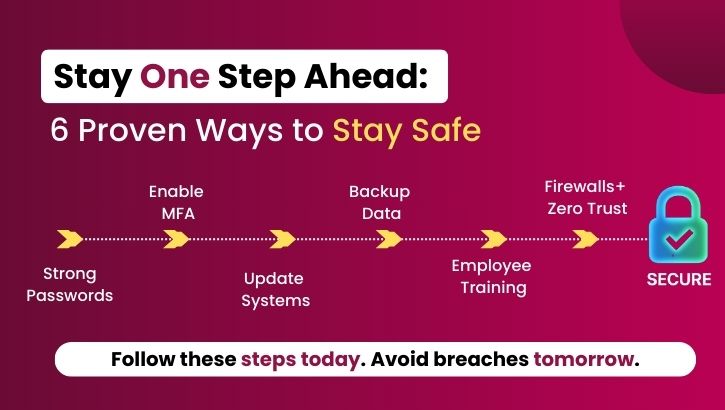
The good news? Most cyberattacks can be prevented with the right habits and tools. Here are some proven best practices:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Avoid common passwords like “123456.” Use a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols, and never reuse the same password across multiple accounts. Consider using a password manager.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a one-time code sent to your phone.
3. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Outdated software is a hacker’s playground. Regularly update your operating systems, browsers, and apps to patch vulnerabilities.
4. Backup Your Data Regularly
Use cloud storage or offline backups to keep your data safe in case of ransomware attacks or accidental loss.
5. Educate Employees
For businesses, human error is the leading cause of data breaches. Regular cybersecurity training helps employees recognize phishing attempts and suspicious activity.
6. Implement Firewalls and Antivirus Software
A strong firewall and reliable antivirus solution act as your first line of defense against malware and unauthorized access.
7. Adopt a Zero Trust Approach
“Never trust, always verify.” This model requires strict identity checks and assumes that every device, user, and connection could be compromised.
Key Stat: According to Verizon’s 2024 DBIR, 74% of breaches involve the human element, making employee training one of the most effective defenses.
Businesses are prime targets for cybercriminals because they handle large amounts of sensitive data. A single breach can result in financial loss, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
For instance, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 was $4.45 million globally. This makes cybersecurity investments a necessity, not a luxury.
Companies should develop:
Small businesses are not immune in fact, 43% of cyberattacks target them because they often lack robust security measures.
The cyber security landscape is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
Being proactive and staying updated is the key to surviving the ever-changing threat landscape.
Cyber security is not just an IT issue, it’s a personal and business responsibility. Whether you’re an individual securing your social media accounts or a business protecting sensitive customer data, taking preventive measures today can save you from major losses tomorrow.
Start with strong passwords, enable MFA, keep systems updated, and educate yourself and your team about common threats. The digital world will keep evolving, and so will cybercriminals, but with a solid security foundation, you can stay one step ahead.