


Machine learning isn’t just another tech trend it’s a measurable shift happening across every industry. According to McKinsey, companies using machine learning process see an average revenue boost of 20% and cost reduction of up to 40%. A report by IDC estimates that global AI and machine learning spending will exceed $500 billion by 2027, proving it’s not optional technology anymore it’s infrastructure.
Today, ML powers 91% of top-tier digital products including search engines, fraud detection systems, recommendation engines, autonomous driving algorithms, and large-scale business forecasting models. From Netflix deciding what you watch next to Tesla enabling self-driving navigation, machine learning has quietly become the engine behind modern automation and decision-making.
Yet despite its massive adoption, more than 60% of business leaders admit they don’t fully understand how machine learning process actually works they just know they need it. And that’s the real gap: everyone uses ML, very few understand it.
This article fixes that problem.
You’re about to learn exactly machine learning process how works step by step without sugar-coating, oversimplifying, or throwing random buzzwords around. If you’re tired of shallow explanations and want a precise, real-world breakdown of how ML models learn, predict, adapt, and deploy at scale, keep reading.
Humans are great at intuition and creative thinking. Machines are unbeatable when it comes to:
If your dataset is small, a traditional program works fine. But when you have millions of data points, multiple variables, and unpredictable patterns, writing rule-based code becomes impossible. That’s where ML steps in the system learns patterns directly from the data.
Machine learning process follows one core rule:
Learn patterns from data → Make predictions → Improve over time.
You feed historical data into a model.
The model finds correlations and builds a mathematical representation.
Then it uses that knowledge to make predictions on new, unseen data.
This is the real workflow not the one-liner definition everyone throws around.
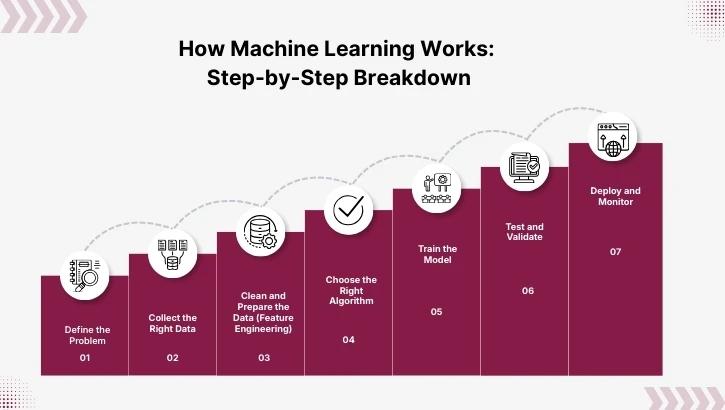
Before touching algorithms, data, or code, you need to define the outcome.
Examples:
A poorly defined problem equals a failed project no matter how good the model is.
Data is the real fuel.
“The world’s most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data. “The Economist
Machine learning needs large, diverse, and relevant data.
Sources include:
Bad data = bad model.
There are no exceptions.
This is the part nobody talks about but takes the most time.
You remove:
Then you transform raw data into usable inputs, known as features.
Example:
Instead of:
“User bought this product”
You generate:
Good features often matter more than the algorithm.
Now the machine learning process starts.
Algorithms fall into three major groups:
| Type of ML | Meaning | Example Algorithms |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Learns from labeled data | Linear Regression, SVM, Random Forest |
| Unsupervised Learning | Finds patterns in unlabeled data | K-means, PCA |
| Reinforcement Learning | Learns by trial and error | Q-learning, Deep RL |
Example use cases:
Training means feeding data to the algorithm repeatedly until it identifies patterns.
The model adjusts internal values (called weights and biases) using mathematical optimization.
If predictions are wrong, the system calculates loss and adjusts until accuracy improves.
Think of it like teaching a kid:
A model isn’t useful if it only memorizes data.
It must generalize.
So, you split data:
Metrics include:
Once approved, the model goes into real use:
Monitoring is critical real-world data changes (called data drift), and models degrade over time. Retraining becomes mandatory.
A Real Example: How Netflix Uses Machine Learning
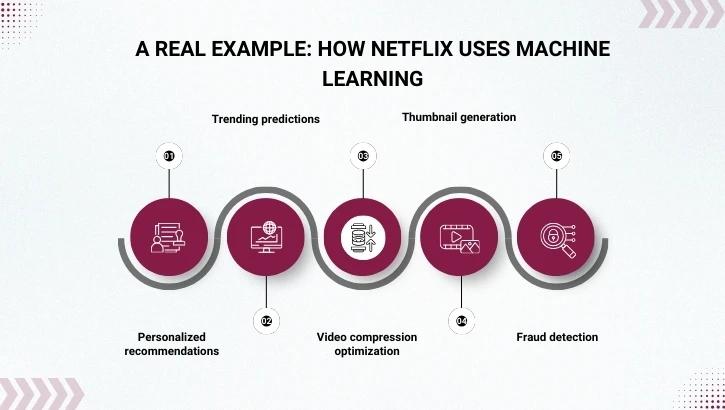
Netflix doesn’t guess what you like it predicts.
ML is used for:
Netflix reported a $1B+ annual revenue increase due to personalized recommendations (source: Netflix Tech Blog).
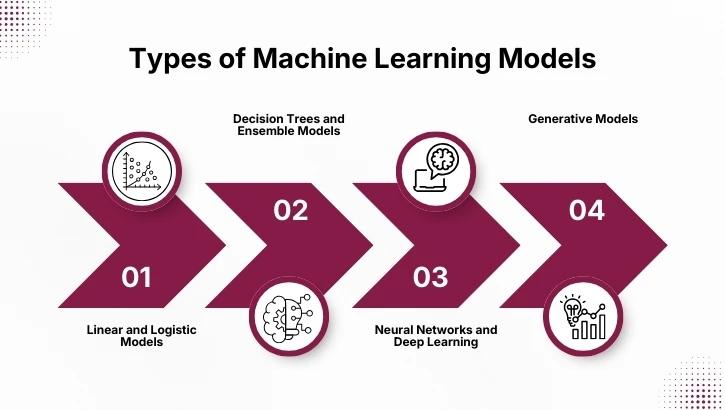
1. Linear and Logistic Models
Simple, fast, strong baseline models.
Used for forecasting, financial models, classification.
2. Decision Trees and Ensemble Models
Algorithms like Random Forest and XGBoost are industry favorites powerful, accurate, and easy to interpret.
3. Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Inspired by the human brain.
Used in:
4. Generative Models
Models like GANs and Transformers create data, not just analyze it.
You interact with ML daily you just don’t realize it.
ML isn’t the future it’s already here.
Benefits of Machine Learning
Limitations (Yes, ML Isn’t Perfect)
If you blindly trust a model you’re asking for failure.
Future of Machine Learning
Machine learning will evolve toward:
AI won’t replace humans but humans who understand AI will replace those who don’t.
Machine learning process works by learning from data identifying patterns, refining predictions, and improving over time. It’s not hype; it’s a practical, scalable solution powering modern technology.
Whether you’re in tech, business, marketing, finance, or healthcare, ignoring machine learning is like ignoring electricity in the 1900s.
The future isn’t humans vs AI it’s humans using AI.